Biology
COMMON EIDER
Central Yup’ik: Mitraq
St. Lawrence Island Yupik: Metghaq
Inupiaq: Amauligruak
Scientific: Somateria mollissima
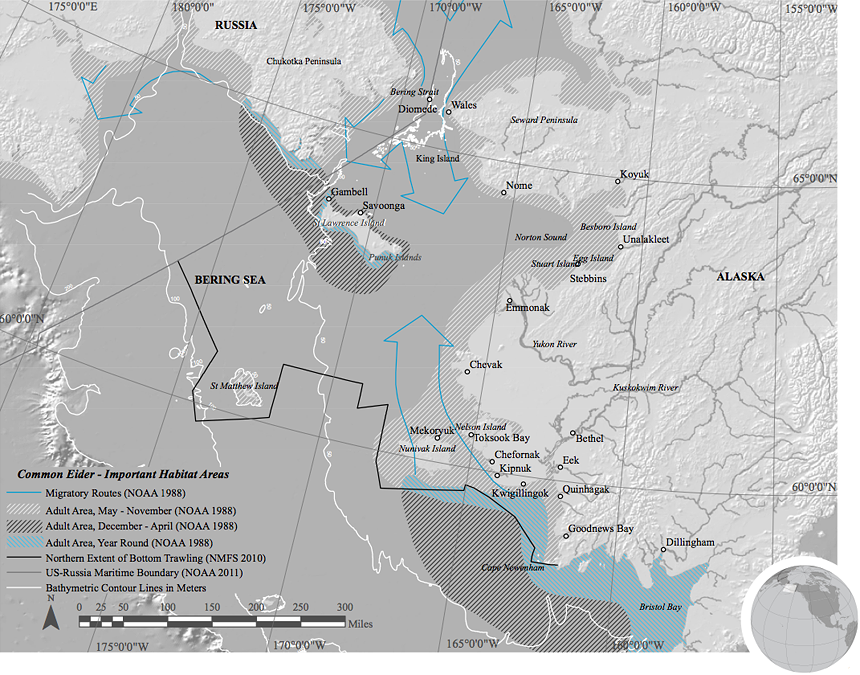
The Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta, Norton Sound, Bering Strait, and the Nunivak, St. Matthew and St. Lawrence islands offer important habitat for millions of migratory birds. Expansive wetlands, lagoons and cliffs are used by huge numbers of shorebirds, seabirds and waterfowl as they travel long distances to their summer breeding grounds every spring.4
Three eider species – spectacled, common and king eiders – remain in the Bering Sea during winter months and are thus featured in this report. From October through March, virtually the entire world population of spectacled eiders is densely packed into open water leads within the ice pack between St. Matthew and St. Lawrence islands.5 Spectacled eiders are listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act; this dynamic marine area is included in their designated critical habitat.
All eider species are benthic feeders with a diet consisting mostly of mollusks, crustaceans and echinoderms. In the summer this diet may be supplemented with plant life.6 Spectacled eiders are capable of diving up to 70 meters (210 feet) to obtain their prey.7 Because of the high energy costs associated with surviving the demanding winter at sea, eiders require abundant sources of the right food to sustain their populations until the spring breeding season begins.8
Other Important Eider Habitats:
Common Eider
King Eider
Spectacled Eider

